Axinite is an uncommon mineral that usually occurs in long, flat, axe-shaped crystals, a trait that makes it highly desirable to collectors who enjoy adding various crystal forms to their collections. Its strong trichroism only adds to its special appeal. As it is rotated, different colors are displayed, including rich cinnamon browns, violets, blues or greens.
General Information
Common Name
Axinite
Species
Axinite
Transparency
Transparent - Translucent
Refractive Index
1.678-1.688
Tolerance:(+0.005/-0.005)
Tolerance:(+0.005/-0.005)
Birefringence
0.010- 0.012
Optic Character
Biaxial
Optic Sign
Negative
Polariscope Reaction
Doubly Refractive (DR)
Fluorescence
SWUV: Inert
LWUV: Inert
LWUV: Inert
Pleochroism
Trichroic, strong violetish purple, light yellow and red-brown
Hardness
6.5-7
Streak
White
Specific Gravity
3.260-3.360 Typical:3.290
Toughness
Varies
Inclusions
Many stones are included some with goethite fibers.
Luster
Vitreous, Greasy
Fracture
Conchoidal, Uneven
Cleavage
Good, in one direction
Chemical Name
calcium aluminum boron sorosilicate hydroxide
Chemical Formula
(Ca,Fe,Mn,Mg)3Al2BSi4O15(OH)
Crystal System
Triclinic
Chemistry Classification
Silicate
Axinite Colors
-
 Blue
Blue -
 Brown
Brown -
 Gray
Gray
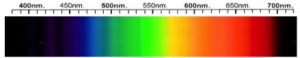
Axinite Spectra
We acknowledge the significant scientific contributions of John S Harris, FGA to the study of gemstone spectra and with deep appreciation to him, acknowledges the use of his images and related notes about gemstones and their spectra in the educational materials on this website.
Countries of Origin
Canada; Russian Federation; Pakistan; Unknown; Brazil