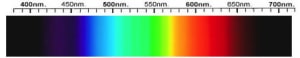
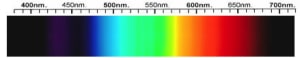
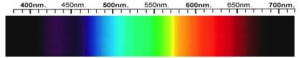
Diopside can be colorless but it most often a bottle green, brownish green or light green. Bright green diopside is commonly known as chrome diopside because of its chromium content. A rare blue variety known as violan may be found in Italy.
General Information
Tolerance:(+0.029/-0.010)
LWUV: inert to weak blue
Diopside Colors
-
 Black
Black -
 Blue
Blue -
 Brown
Brown -
 Colorless
Colorless -
 Green
Green -
 White
White -
 Yellow
Yellow
Diopside Spectra
We acknowledge the significant scientific contributions of John S Harris, FGA to the study of gemstone spectra and with deep appreciation to him, acknowledges the use of his images and related notes about gemstones and their spectra in the educational materials on this website.
Alternate Names
Tashmarine(TM),Shanseres(R), Star Diopside, Cat's-Eye Diopside, Malacolite, Alalite, Violane, Chrome Diopside
Countries of Origin
Papua New Guinea; Angola; Sudan; Kazakhstan; Paraguay; Portugal; Solomon Islands; Greece; Latvia; Mongolia; Morocco; Unknown; Mali; Guatemala; Iraq; Chile; Nepal; Argentina; Ukraine; Zambia; Saint Vincent And The Grenadines; Congo; India; Canada; Turkey; Belgium; Namibia; Finland; South Africa; Bermuda; Georgia; Peru; Turkmenistan; Germany; Yemen; Tanzania, United Republic Of; Eritrea; Viet Nam; Madagascar; Thailand; United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland; Libya; Sweden; Malawi; Saint Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha; Poland; Bulgaria; Jordan; Nigeria; Palestine, State of; Croatia; Syrian Arab Republic; Sri Lanka; Timor-Leste; United Arab Emirates; Kenya; Switzerland; Spain; Azerbaijan; Cuba; Burkina Faso; Mauritania; Congo (the Democratic Republic of the); Israel; Australia; Tajikistan; Myanmar; Cameroon; Cyprus; Malaysia; Iceland; Oman; Bosnia And Herzegovina; Armenia; Austria; Mozambique; Korea (the Republic of); Brazil; Algeria; Cabo Verde; Jersey; Lesotho; Colombia; Ecuador; Iran (Islamic Republic of); Hungary; Republic of Kosovo; South Sudan; Japan; Mauritius; Taiwan (Province of China); Albania; Bolivia (Plurinational State of); Lao People's Democratic Republic; New Zealand; Senegal; Italy; Antarctica; Ethiopia; Haiti; Macedonia (the former Yugoslav Republic of); Afghanistan; Russian Federation; Czechia; United States of America; Egypt; Sierra Leone; Saudi Arabia; Netherlands; Pakistan; China; Ireland; Slovakia; France; Lithuania; Serbia; Kyrgyzstan; Cote D'Ivoire; Romania; Philippines; Uzbekistan; Bangladesh; Nicaragua; Norway; Botswana; Denmark; Dominican Republic; Mexico; Uganda; Zimbabwe; Greenland; Montenegro; Indonesia
Care
Cleaves easily, or is known to brittleness. Avoid ultrasonic cleaners. Wear with care.
Optical Phenomena
Cat's Eye
The term cat's eye, or chatoyancy, is used to describe a phenomenal optical property in gemstones, in this case diopside. The effect, when present, appears as a bright, narrow slit similar to the pupils in the eyes of your favorite feline. This phenomenon is caused by parallel fibrous or needle-like inclusions that interfere with the passage of light through the crystal, scattering and reflecting light back to the viewer as a thin line.
LWUV: possibly green
Star
Star diopside exhibits the optical phenomenon called asterism, a star-like pattern created on the surface of a gemstone when light encounters parallel fibrous, or needle-like, inclusions within its crystal structure. Light that strikes the inclusions within the gem reflects off of the inclusions, creating a narrow band of light. When two or more intersecting bands appear, a star pattern is formed. Depending on the crystal, the star may have four, six, or even twelve rays. When only one band forms, it is classified as a "cat's eye."
Tolerance:(+0.029/-1.701)
LWUV: Inert