Glass has been used for thousands of years as a decoration. It is sometimes employed as a gemstone simulant, but is often appreciated entirely upon its own merits, especially when formed with a high level of artistry.
General Information
Tolerance:can go OTL
LWUV: Variable
Glass Colors
-
 Bi-color
Bi-color -
 Black
Black -
 Blue
Blue -
 Brown
Brown -
 Colorless
Colorless -
 Gray
Gray -
 Green
Green -
 Green
Green -
 Green
Green -
 Multi-color
Multi-color -
 Orange
Orange -
 Pink
Pink -
 Purple
Purple -
 Red
Red -
 White
White -
 Yellow
Yellow
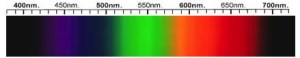
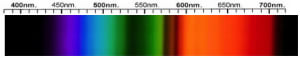
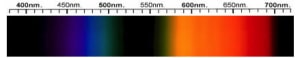
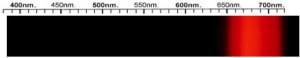
Glass Spectra
We acknowledge the significant scientific contributions of John S Harris, FGA to the study of gemstone spectra and with deep appreciation to him, acknowledges the use of his images and related notes about gemstones and their spectra in the educational materials on this website.
Alternate Names
Paste, Strass, Faience
Countries of Origin
Papua New Guinea; Cambodia; Kazakhstan; Paraguay; Bahamas; Solomon Islands; Montserrat; Unknown; Mali; Marshall Islands; Guadeloupe; Panama; Bonaire, Sint Eustatius and Saba; Argentina; Seychelles; Belize; Zambia; Bahrain; Congo; Guinea-Bissau; Saint Barthelemy; Namibia; Comoros; Faroe Islands; Finland; Georgia; Yemen; Tanzania, United Republic Of; Eritrea; Puerto Rico; Viet Nam; Aruba; Madagascar; Libya; Sweden; Cocos (Keeling) Islands; Malawi; Andorra; Saint Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha; Liechtenstein; Poland; Bulgaria; Jordan; Tunisia; Tuvalu; United Arab Emirates; Kenya; French Polynesia; Djibouti; Lebanon; Azerbaijan; Cuba; Mauritania; Saint Lucia; Guernsey; Congo (the Democratic Republic of the); Mayotte; Israel; San Marino; Australia; Tajikistan; Myanmar; Cameroon; Gibraltar; Cyprus; Northern Mariana Islands; Malaysia; Iceland; Oman; Bosnia And Herzegovina; Armenia; Gabon; Korea (the Republic of); Luxembourg; Brazil; Turks and Caicos Islands; Algeria; Cabo Verde; Jersey; Slovenia; Colombia; Ecuador; Iran (Islamic Republic of); Lao People's Democratic Republic; Vanuatu; United States Minor Outlying Islands; Honduras; Italy; Antarctica; Nauru; Haiti; Afghanistan; Burundi; Russian Federation; Singapore; French Guiana; American Samoa; Christmas Island; Netherlands; China; Martinique; Kyrgyzstan; Reunion; Saint Pierre And Miquelon; Cote D'Ivoire; Bhutan; Multiple; Romania; Falkland Islands [Malvinas]; Togo; Philippines; Uzbekistan; Pitcairn; Zimbabwe; British Indian Ocean Territory; Montenegro; Dominica; Indonesia; Benin; Angola; Virgin Islands (British); Sudan; Brunei Darussalam; Portugal; New Caledonia; Grenada; Moldova (the Republic of); Cayman Islands; Greece; Latvia; Mongolia; Morocco; Guatemala; Guyana; Iraq; Chile; Nepal; Isle of Man; Ukraine; Ghana; Holy See; Anguilla; Saint Vincent And The Grenadines; India; Canada; Maldives; Turkey; Belgium; South Africa; Bermuda; Aland Islands; Central African Republic; Jamaica; Peru; Turkmenistan; Venezuela (Bolivarian Republic of); Germany; Fiji; Tokelau; Hong Kong; Guinea; Chad; Somalia; Thailand; United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland; Equatorial Guinea; Kiribati; Costa Rica; Saint Martin (French part); Kuwait; Nigeria; Palestine, State of; Croatia; Sao Tome And Principe; Syrian Arab Republic; Cook Islands; Sri Lanka; Uruguay; Timor-Leste; Switzerland; Samoa; Spain; Liberia; Burkina Faso; Swaziland; Palau; Estonia; Wallis and Futuna; Niue; Svalbard And Jan Mayen; Austria; Mozambique; El Salvador; Monaco; Guam; Lesotho; Tonga; Heard Island And Mcdonald Islands; Western Sahara; Hungary; Republic of Kosovo; South Sudan; Japan; Belarus; Curacao; Mauritius; Taiwan (Province of China); Bouvet Island; Albania; Bolivia (Plurinational State of); Norfolk Island; Trinidad And Tobago; Virgin Islands (U.S.); New Zealand; Sint Maarten (Dutch part); Senegal; Micronesia (Federated States of); Ethiopia; Macedonia (the former Yugoslav Republic of); Czechia; United States of America; Egypt; Sierra Leone; Malta; Saudi Arabia; South Georgia And The South Sandwich Islands; Pakistan; Gambia; Ireland; Qatar; Slovakia; France; Lithuania; Serbia; Niger; Rwanda; Saint Kitts And Nevis; French Southern Territories; Bangladesh; Barbados; Nicaragua; Norway; Botswana; Macao; Denmark; Dominican Republic; Mexico; Uganda; Suriname; Greenland; Antigua And Barbuda
History
Although glass isn't technically a gemstone, it's used so often as a simulant and in beads we feel it's worthy of listing. Most glass is man-made and has a hardness of 5 – 5 1/2 on the Mohs scale. It's made from sand that is almost pure silicon dioxide, with a few proprietary additives to adapt for temperature and color. Glass is a go-to product for jewelry due to its versatility. It can be colored, twisted, textured, sand-blasted, bent and even faceted. In short, glass is limited in design only by the imagination. It can simulate most gemstones. The downside is that glass is fragile and can be worn away over time. It's best suited for necklaces and earrings. If your bracelets and rings are made of glass, exercise care when you wear them. Glass pieces should always be stored in a well-protected space.
Care
Normal, gentle care
Optical Phenomena
Color Change
This man-made jewel is unique in that is displays the optical phenomenon of color change. Although this is not a natural phenomenon, it is an affordable alternative to rare and expensive color change gems, such as alexandrite. You can observe color change in this jewel by viewing it interchangeably in natural and incandescent light.
Cat's Eye
The term cat's eye, or chatoyancy, is used to describe a phenomenal optical property in gemstones, in this case man-made glass. The effect, when present, appears as a bright, narrow slit similar to the pupils in the eyes of your favorite feline. This phenomenon is caused by parallel fibrous or needle-like inclusions that interfere with the passage of light through the crystal, scattering and reflecting light back to the viewer as a thin line.Although in this case the phenomenon is not natural, it offers an affordable alternative to this rare phenomenon seen with some natural gems.