Rhodolite is a mixture of pyrope and almandite garnets. The color ranges from pinkish purple to reddish purple. The name is derived from the Greek rhodon (rose) and lithos (stone). The most popular varieties of rhodolite garnet are grape color garnet and raspberry garnet. It has long been a favorite in the jewelry market.
General Information
LWUV: Inert
Rhodolite Colors
-
 Pink
Pink -
 Pink
Pink -
 Purple
Purple -
 Red
Red -
 Red
Red
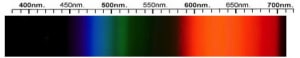
Rhodolite Spectra
We acknowledge the significant scientific contributions of John S Harris, FGA to the study of gemstone spectra and with deep appreciation to him, acknowledges the use of his images and related notes about gemstones and their spectra in the educational materials on this website.
Alternate Names
Grape Color Garnet, Raspberry Garnet
Countries of Origin
Tanzania, United Republic Of; Afghanistan; Sri Lanka; United States of America; Madagascar; Zambia; Kenya; Thailand; French Polynesia; India; Mozambique; Unknown; Malawi; China; Brazil; South Africa; Nigeria
History
Rhodolite was first described in the article On Rhodolite, a New Variety of Garnet by W.E. Hidden and J.H. Pratt in 1898 in the American Journal of Science. Most material today comes from the "Mozambique Belt" in Africa.
Care
Normal Care
Optical Phenomena
Cat's-Eye Rhodolite
Star or Cat's-Eye Rhodolite
Star or cat’s-eye rhodolite garnet exhibits optical phenomenon when light within the gem reflects off the rutile inclusions, creating narrow bands of light. When two or more intersecting bands appear, a star pattern is formed. Depending on the crystal, the star may have four or six rays. Stones have been reported with diasterism where both a 4-ray and a 6-ray star can be seen depending on the light orientation. The phenomenon comes from needle-like inclusions oriented at 70 and 110 degrees angles. When only one band forms, it is classified as a "cat's eye". Rhodolite star garnet comes from Kangala Mine, in the Tiriri mining district, Tanzania. The largest stone found from the Kangala Mine is 15.60ct.